New Arrivals 1220X2440mm 12mm MDF Boards/20mm Thick MDF Board From China
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | MDF7 |
| Type | MDF / Semi-hardboards |
| Finish | Melamine Impregnated Paper |
| Formaldehyde Emission Standards | E1 |
| Usage | Indoor |
| Production Process | Dry-Proces |
| Size | 1220*2440/1250*2500 or as Request |
| Thickness | 18mm |
| Certification | BS, MSDS, CARB, CE, ISO, ISO9001, CE |
| Tolerance | +-0.2mm in The Thickness |
| Product Name | MDF |
| Moisture Content | 6~8% |
| Glue | E1, E0,P2 |
| Density | 730kg/Cbm |
| Grade | First-Class |
| Shape | Square |
| Surface Finishing | Finished |
| Slab Structure | MDF, HDF |
| Transport Package | Standard Export Package |
| Specification | 1220X2440mm |
| Trademark | TREEZO LOGO |
| Origin | Linyi City, Shandong, China |
| HS Code | 4401210010 |
| Production Capacity | 300000 Cbm Per Year |
Packaging & Delivery
Package Size 125.00cm * 245.00cm * 100.00cm Package Gross Weight 1000.000kgProduct Description
Product Description
| Product Number | MDF 7 | Brand Name | Treezo |
| Main Material | Poplar | Application | Hotel, Hotel, Villa, Apartment, Office Building |
| Color | Natural | Design | Modern |

Medium-density fibreboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibres, often in a defibrator, combining it with wax and a resin binder, and forming it into panels by applying high temperature and pressure.[1] MDF is generally denser than plywood. It is made up of separated fibres but can be used as a building material similar in application to plywood. It is stronger and denser than particle board.Physical propertiesOver time, the term "MDF" has become a generic name for any dry-process fibre board. MDF is typically made up of 82% wood fibre, 9% urea-formaldehyde resin glue, 8% water, and 1% paraffin wax.[4] The density is typically between 500 and 1,000 kg/m3 (31 and 62 lb/cu ft).[5] The range of density and classification as light-, standard-, or high-density board is a misnomer and confusing. The density of the board, when evaluated in relation to the density of the fibre that goes into making the panel, is important. A thick MDF panel at a density of 700-720 kg/m3 (44-45 lb/cu ft) may be considered as high density in the case of softwood fibre panels, whereas a panel of the same density made of hardwood fibres is not regarded as so. The evolution of the various types of MDF has been driven by differing need for specific applications.In Australia and New Zealand, the main species of tree used for MDF is plantation-grown radiata pine, but a variety of other products have also been used, including other woods, waste paper, and fibres. Where moisture resistance is desired, a proportion of eucalypt species may be used, making use of the endemic oil content of such trees.Chip productionThe trees are debarked after being cut. The bark can be sold for use in landscaping or used as biomass fuel in on-site furnaces. The debarked logs are sent to the MDF plant, where they go through the chipping process. A typical disk chipper contains four to 16 blades. Any resulting chips that are too large may be rechipped; undersized chips may be used as fuel. The chips are then washed and checked for defects. Chips may be stored in bulk, as a reserve for manufacturing.Fibre productionCompared to other fibre boards, such as Masonite, MDF is characterised by the next part of the process, and how the fibres are processed as individual, but intact, fibres and vessels, manufactured through a dry process.The chips are then compacted into small plugs using a screw feeder, heated for 30-120 seconds to soften the lignin in the wood, then fed into a defibrator. A typical defibrator consists of two counter-rotating discs with grooves in their faces. Chips are fed into the centre and are fed outwards between the discs by centrifugal force. The decreasing size of the grooves gradually separates the fibres, aided by the softened lignin between them.From the defibrator, the pulp enters a blowline, a distinctive part of the MDF process. This is an expanding circular pipeline, initially 40 mm in diameter, increasing to 1500 mm. Wax is injected in the first stage, which coats the fibres and is distributed evenly by the turbulent movement of the fibres. A urea-formaldehyde resin is then injected as the main bonding agent. The wax improves moisture resistance and the resin initially helps reduce clumping. The material dries quickly in the final heated expansion chamber of the blowline and expands into a fine, fluffy and lightweight fibre. This fibre may be used immediately, or stored.Sheet formingDry fibre gets sucked into the top of a "pendistor", which evenly distributes fibre into a uniform mat below it, usually of 230-610 mm thickness. The mat is precompressed and either sent straight to a continuous hot press or cut into large sheets for a multiple-opening hot press. The hot press activates the bonding resin and sets the strength and density profile. The pressing cycle operates in stages, with the mat thickness being first compressed to around 1.5 times the finished board thickness, then compressed further in stages and held for a short period. This gives a board profile with zones of increased density, thus mechanical strength, near the two faces of the board and a less dense core.After pressing, MDF is cooled in a star dryer or cooling carousel, trimmed, and sanded. In certain applications, boards are also laminated for extra strength.The environmental impact of MDF has greatly improved over the years.Today, many MDF boards are made from a variety of materials. These include other woods, scrap, recycled paper, bamboo, carbon fibres and polymers, forest thinnings, and sawmill off-cuts.As manufacturers are being pressured to come up with greener products, they have started testing and using nontoxic binders. New raw materials are being introduced. Straw and bamboo are becoming popular fibres because they are a fast-growing, renewable resource.
Detailed Photos
Certifications


Packaging & Shipping
1. Inner packing: Inside pallet is wrapped with a 0.20mm plastic bag2.Outer packing: Pallets are covered with 3mm package plywood or carton and then steel tapes for strengthening
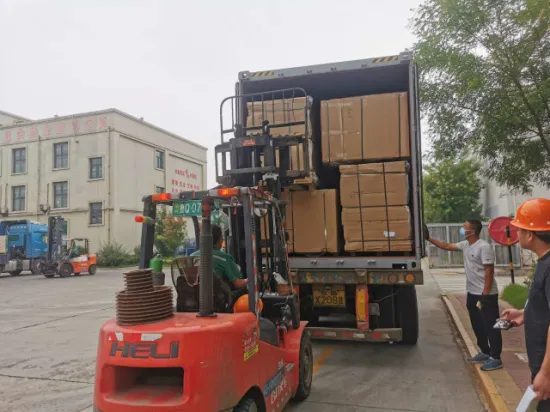
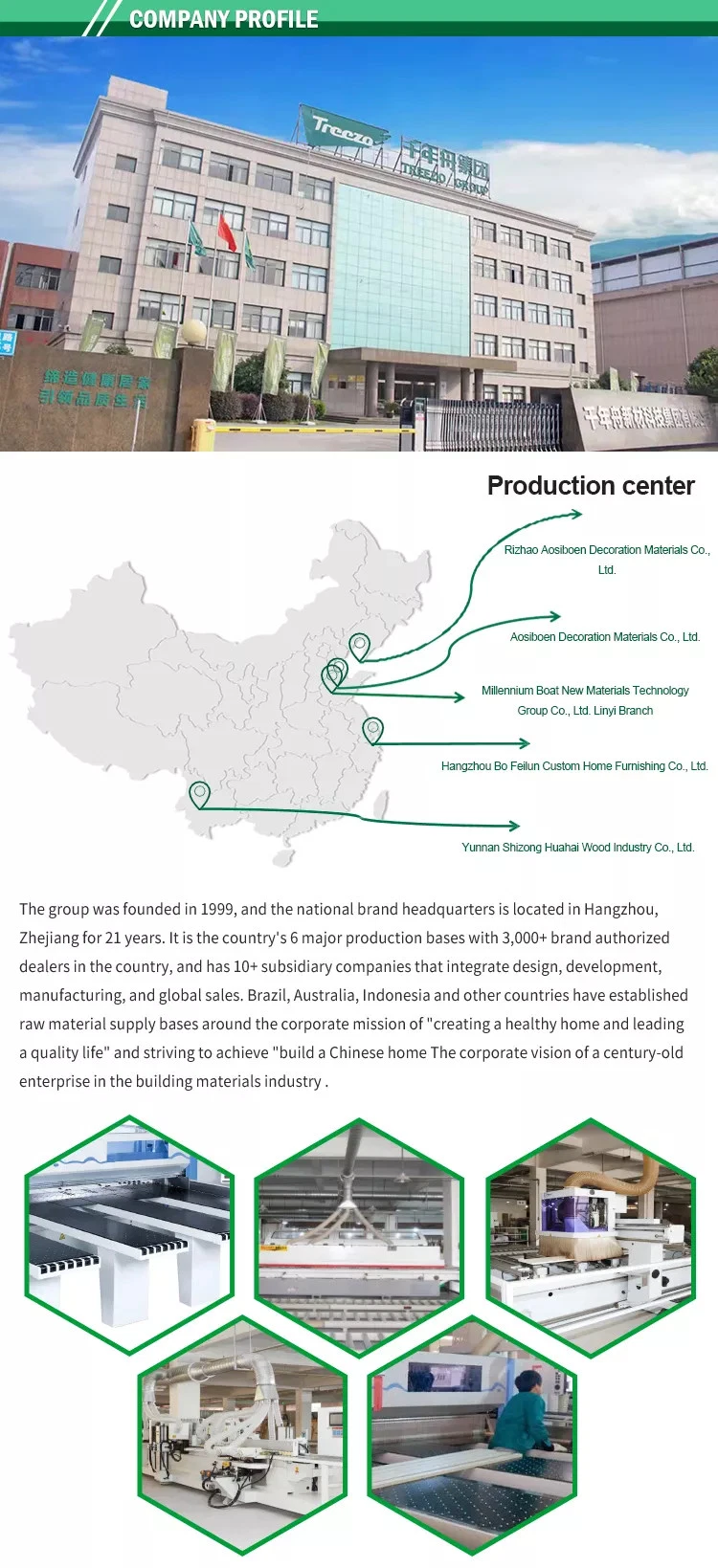
Our Factory
FAQ
Q1: Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A1: We are manufacturing company who is specialized in producing all kinds of OSB,MDF Board,Birch Plywood,Commercial Plywood,Film Faced
,Plywood,Marine Plywood and other wooden product.
Q2: What's your MOQ?
A2: Our MOQ is 20'GP, any small trial order is also welcomed and can be in a further discussion.
Q3: Do you provide samples?
A3: yes, we can. The sample will be cost 1.5 times of its original price but the extra cost will be refund you once you place the order.
Q4: what's your payment terms and trade terms?
A4: 30%T/T deposit before production, the balance 70% against the copy of B/L. FOB /CIF/CNF Price or other request.
Q5:how can we guarantee quality?
A5:Always a pre-production sample before mass production;Always final Inspection before shipment.